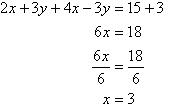The 'perpendicularity' can be with planes or lines.
When one speaks about lines, two lines could be declared as perpendicular in two ways:
- One when the angle between them is 90 degree and so is the congruent angle too.
- Other, when the lines satisfy the condition of the perpendicularity with respect to slope.
- One when the line is having an x coordinate value = 0 and some value for the y coordinate ( a line which would be parallel to the x-axis)
- Another when the line is having an y coordinate value = 0 and some value for the x coordinate ( a line which would be parallel to the y-axis)
- Another when the product of the slopes of both the lines result in -1.(minus 1)